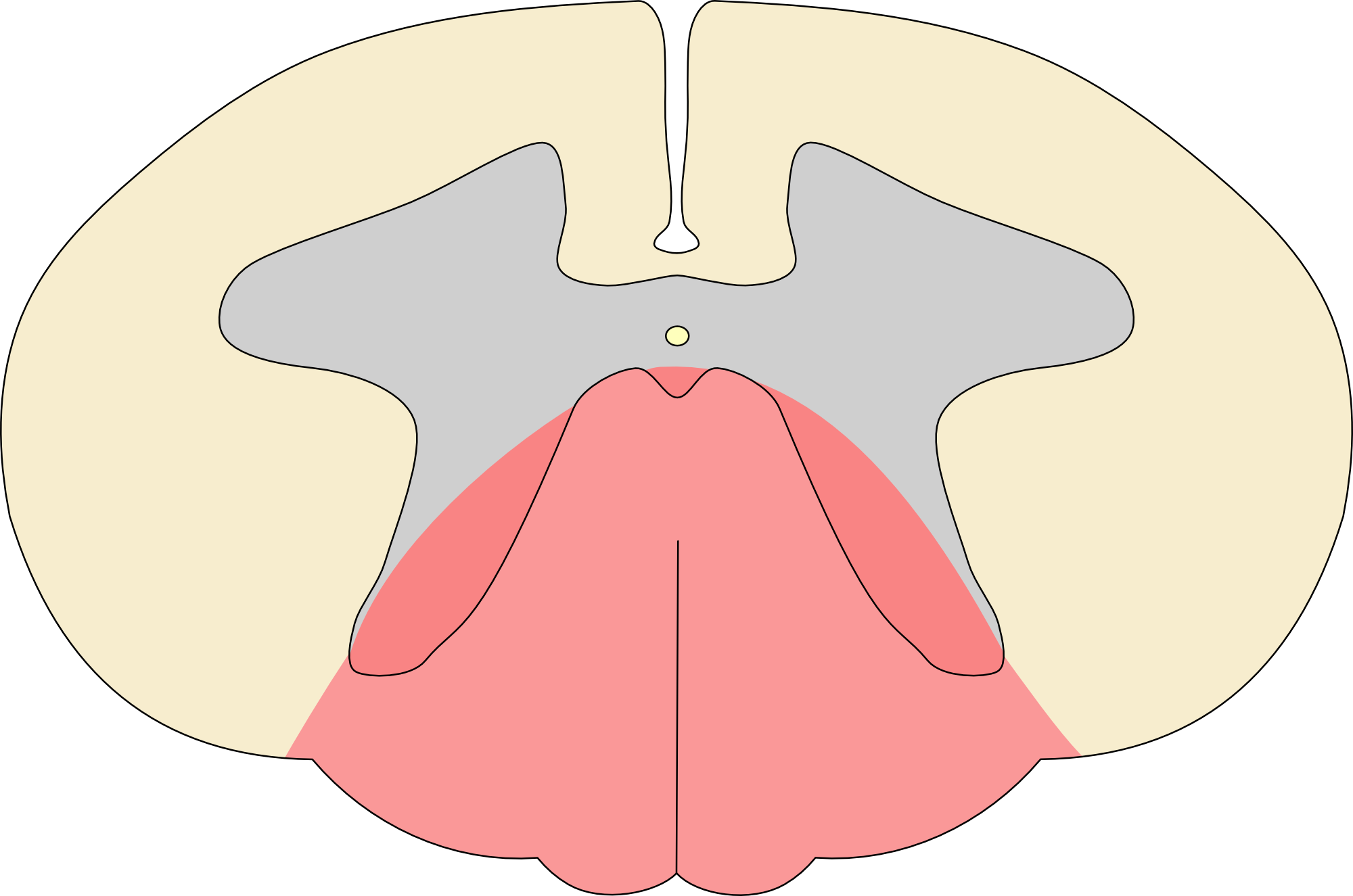
Posterior spinal cord syndrome
Causes
- Ischemia
- Aortic pathology (dissection, aneurysm, thrombosis, iatrogenic injury)
- Anterior spinal artery dissection (traumatic, iatrogenic) due to ischemia in collaterals or watershed infarction in the posterior cord
- Fibrocartilaginous embolism from intervertebral disk
- Cholesterol embolism
- Vasculitis
- Hypertensive small vessel disease
- Sickle cell anemia
- SLE
- Atrial myxoma
- Intra-aortic balloon pump
- Lumbar artery compression
- Disk herniation
- Neoplasm
- Penetrating trauma
- Spinal fracture dislocation
- Epidural abscess or hematoma
- Carcinomatous meningitis
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Thoracotomy and thoracoplasty
- Esophageal surgery
- Lumbar sympathectomy
- Celiac plexus block
Clinical presentation
- Loss of proprioception and vibration sensation
- Preserved pain and temperature sensation
- Loss of reflexes below involved segments
- Intact motor function in pure posterior spinal cord syndrome
- Focal motor and/or sensory deficits in extremities might represent lacunar spinal cord infarcts
- Slowly progressive para- or quadriparesis in hypoxic myelopathy
- Spinal cord claudication in hemodynamic transient ischemic attacs